- +877 776 0673
- [email protected]
- Mon - Fri: 9:00 - 18:00 EST

There are two types of people in the world, those who fish and those who do not.
The type of fishing technique you use will determine the type, quantity, and quality of fish you will catch.
There are many techniques, but you could primarily catch a fish by hand, using spears, giant nets, small nets, or a hook.
And just like fishing, phishing also has many different techniques to trick unsuspecting people into sharing their data.
Depending on the technique, the results will differ. Here are the main types of phishing techniques that are used by hackers today:
With over 96% phishing attacks, the most common phishing technique arrives by email[1].
Phishers send legitimate-looking emails that appear as though they originated from reputable brands that many people do business and trust like BestBuy, Amazon, Federal Express, DHL, and PayPal.
The emails often ask customers to confirm information or to go to the business site by clicking on a provided link and often include a statement of impending consequences if you fail to act.
While both phishing and spear phishing share similar techniques, they differ in objectives.
Phishing is more like an exploratory attack that casts many people, like fishing with a net. In comparison, spear phishing is more precise and target-specific.
In spear phishing, an email is crafted and sent to a specific person within an organization with the sole purpose of infecting their system with malware (more on this below) to obtain sensitive information.
The main objective of spear phishing is to attack large companies or high-value corporate employees, which often lead to a much sophisticated and targeted attack.
Web-based delivery is one of the most sophisticated phishing techniques. Also known as “man-in-the-middle (MITM),” the phisher intercepts the communication between the unsuspecting user and the original website that they are surfing.
The phisher decodes the communication traffic between the intended website and the end-user.
As the user continues to surf and pass sensitive information, the phishers gather the data without the user knowing about it.
The easiest and most common way of a MITM attack is to give free WIFI. The hacker sets up a malicious free WIFI hotspot, which is not password protected. Once you log into the network, the attacker will have complete visibility of all your online activities.
Link manipulation is the technique in which the phisher sends a link to a malicious website, typically a look-a-like website.
When the unsuspecting end-user clicks on the deceptive link, it opens up the phisher’s website instead of the intended website, which looks the same.
Keyloggers refer to the malware used to identify input from the keyboard like someone looking over your shoulder and reading every key you hit.
The information is sent directly to the hackers who will decipher passwords and other types of information.
Phishing scams involving malware require it to execute on the unsuspecting user’s computer.
The malware is usually attached to the email sent to the user by the phishers. Once you click on the link, the malware will start functioning.
A Trojan horse is a type of malware designed to mislead the user with an action that looks legitimate but allows unauthorized access to the user account to collect credentials through the local machine.
Phishing is not the end of a hack unless you are the target.
It’s the start of the hack where the intended target is a wealthy multinational company.
As someone who enjoys fishing, I understand that if I want to catch a big fish, I will have to leverage a small fish as bait.

It’s the start of the hack where the intended target is a wealthy multinational company.
As someone who enjoys fishing, I understand that if I want to catch a big fish, I will have to leverage a small fish as bait.
Please help me transfer millions of dollars?
This is a type of phishing strategy called a “fund transfer” fraud reaches victims by email.
Most of you reading this is thinking, “Edwin, I knew it was a scam.”
Great, but did you know that it’s one of the longest-running online scams which generates over $700,000 per year?
Phishing messages are always of an “urgent, private” nature.
Here is an example of a phishing attempt I recently received.
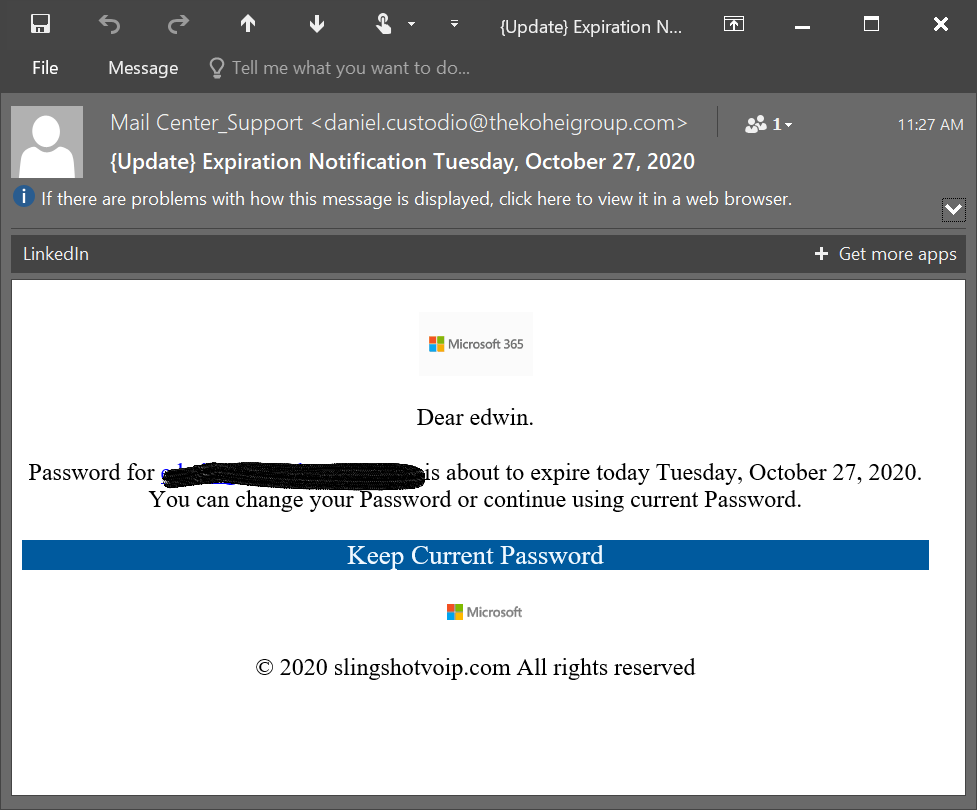
Typical data that hackers are looking to get during a phishing attack are:
The above email looks real, and if I were not privy to phishing attacks, I would click the link, verifying that I am a Microsft user, my email address and password.
I would’ve also given the hacker access to my email address where they could masquerade as me, emailing co-workers, clients, colleagues and friends.
To give you an idea of how widespread phishing is and how much companies stand to lose from a successful attack:
The average cost of a phishing attack to a mid-sized company is $1.6 million.
The best policy to protect yourself and your business from a phishing attack are to be vigilant, aware and suspicious of all emails. Be wary that hackers are relentless and are playing the numbers game, it could be not if you get hacked, when.
Suppose a phishing attack compromises your company. In that case, you have to be sure to have a business continuity plan(BCP) in place to recover to minimize the impact and get back to business.
Want to learn more? Read these related articles:
Please click Like if you found value in this article. Click Share to spread the love, thank you!